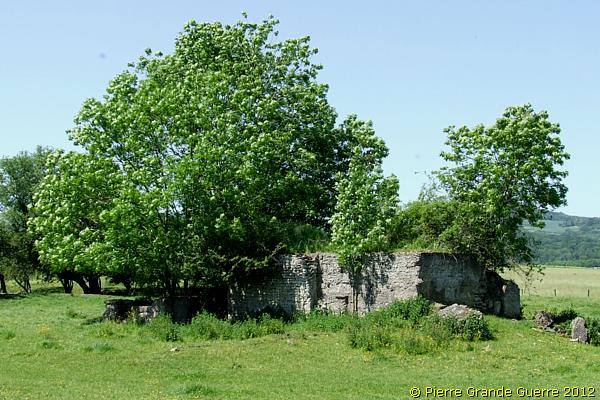
VOSGES - Mutzig - Fort de Mutzig - Feste Kaiser Wilhelm II
SPECIAL Photo Impression - Year of visit: 2010

From Badonviller or the Col du Donon we continue north-eastward for a visit to an extraordinarily well restored sample of German fortifications: the Feste Kaiser Wilhelm II, or Fort de Mutzig, lying on a height, some 8 km. away from the 1871-1918 Franco-German Border.
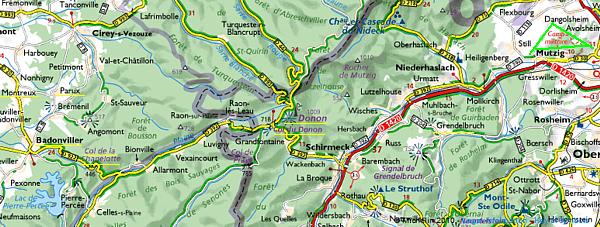
We enter the Feste Kaiser Wilhelm II (F-KWII) ...

... at the northern side of the height via the L-shaped, dry moat.

Before we continue exploring the fortress, ...

... I present you a concise reminder about the battles of August and September 1914.
French Operations in August 1914
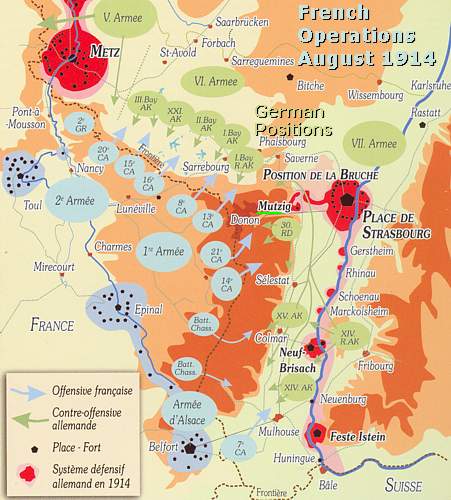
At the
beginning of the Great War General Joffre launched Plan XVII, a kind of
pre-emptive strike to re-conquer the lost Alsace Lorraine sector.
From 6 August Joffre launched 3 Armies in Alsace Lorraine; General
Ruffey
and his 3rd Army near Metz,
General
Castelnau
and this 2nd Army near
Nancy, and General
Dubail
and his 1st Army
near
Epinal
and the "
Crêtes
",
the summits of the Vosges.
They were opposed by the Bavarian 6th Army of
Crownprinz
Rupprecht
von Bayern, and the 7th Army of
General von
Heeringen
.
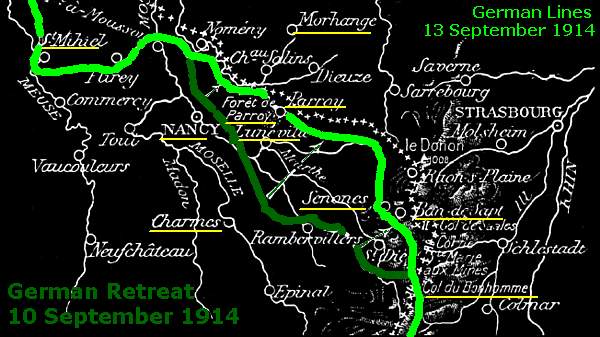
German Counteroffensives - 20 August - 11 September 1914
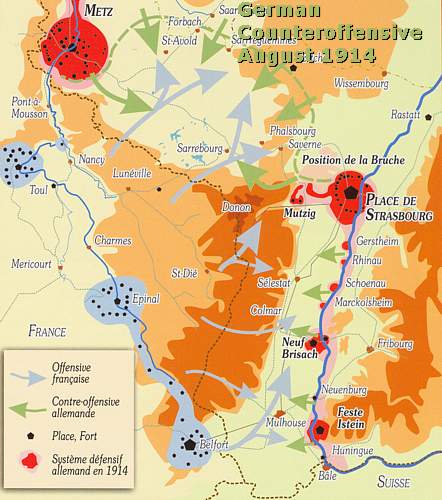
After the first
successes of the French 1st and 2nd Army in Alsace Lorraine, the
Germans decided to counterattack the two French Armies. On 20 August
1914 Crown Prince
Rupprecht
Von Bayern's 6th
Army attacked General
Castelnau's
2nd Army.
Also on 24 August General Von
Heeringen's
7th
Army launched, south of the
Trouée
des
Charmes
, the Battle of the Haute
Meurthe
-
Mortange
, at
three mountain passes in the Northern Vosges, at the left flank of
General
Dubail's
1st Army.
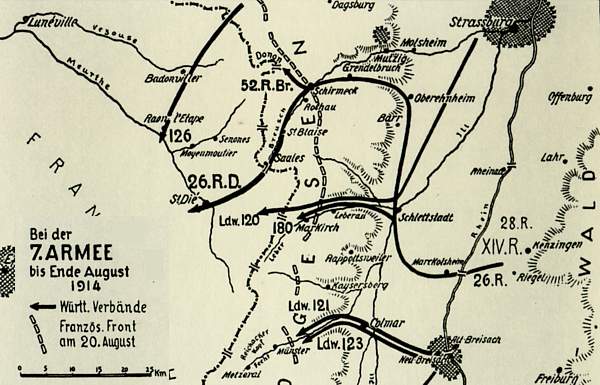
The Battle for
the Grand
Couronné
, which started at 31
August, was not successful at all for the German 6th Army. At 10
September the Germans decided to withdraw the 6th Army. Under pressure
of General's Foch's 20th Army Corps the Germans retreated from Nancy to
behind the German border of 1871-1918.
(Read for more
details about the Battle of the Haute Meurthe - Mortange and the Battle for the Grand Couronné my pages about Col du
Bonhomme
and La
Chipotte
- La
Chapelotte
.)
The next frame contains some concise information, ...

... about the Fort de Mutzig - Feste Kaiser Wilhelm II, for better understanding this complex and it's purpose.

Fort de Mutzig - Feste Kaiser Wilhelm II - 1893-1918 - Introduction
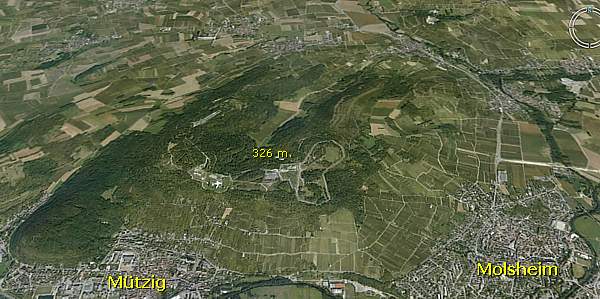
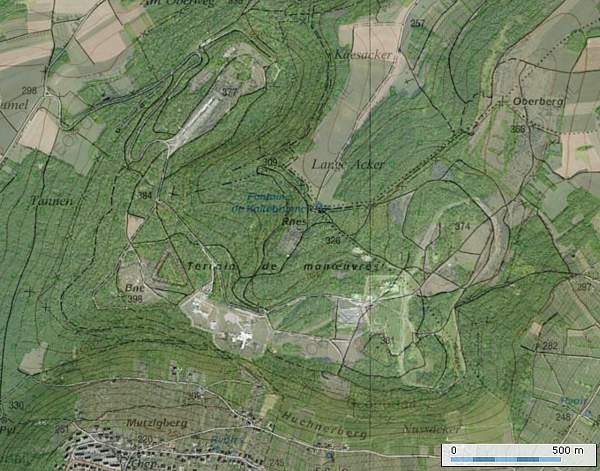
In January 1893, Kaiser Wilhelm II himself decided to build a fortress on a 330 m. height above the village of Mutzig and the town of Molsheim , Alsace.

Four months later, in April, the first construction works began.
Along with the fortified belt of Strasbourg, the fort barred the way of the Alsatian plain between Strasbourg and the Vosges Mountains, hindering French troops advancing from the west and south to Strasbourg and Metz.
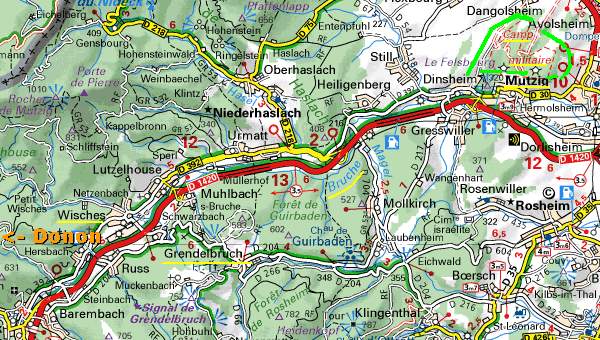
As a forward outpost of the fortifications of Strasbourg, some 8 km, from the border, the Feste Kaiser Wilhelm II guarded the valley of the Bruche -river, and the Grendelbruch east of the Donon .
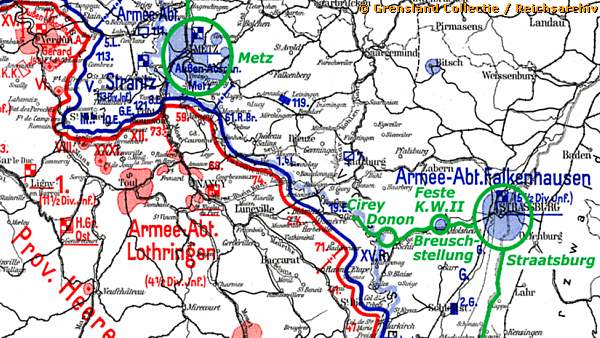
The fortress formed a forward component of the German " Breusch-Stellung ". ( la Bruche -river means in German “ Breusch ”).
The construction of the Feste Kaiser Wilhelm II
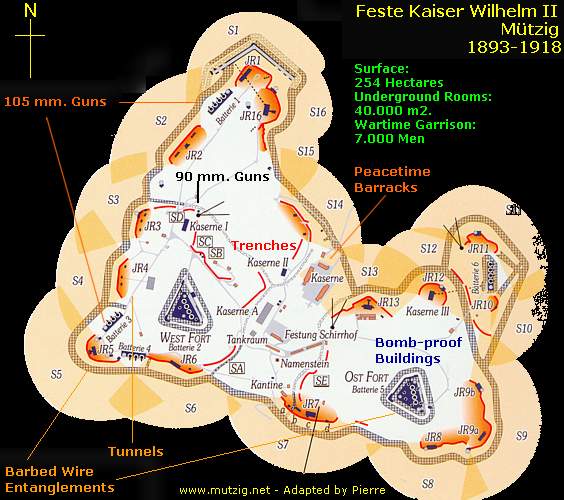
This fortress started a new era in German fortification building. The first plans called for five enclosed "unit-forts". The construction started with the central Peacetime Barracks.

At the same time the Germans constructed two forts in a triangular shape: the East Fort (1893) and the West Fort (1895). Both forts possess each four 150 mm. guns and light 57 mm. artillery guns; six 5 cm. guns in the East Fort, and two in the West Fort.

Due to the high construction costs the building plans changed from 1900. The next two fortifications were built on a new concept. Instead of enclosing all assets in one fort, they were dispersed in many constructions, vast redoubts, connected by underground tunnels. The firing batteries, shelters, and observations posts were better armored than in a fort, which was traditionally designed during the period before 1900.

After 1900 three batteries of each four 105 mm. guns were added along the west side of the height. In total the Feste possessed 22 artillery guns, covered by an armored cupola. All fortifications were guarded by trenches or breastworks, “ Schützengraben ”, marked “S1”, S16”, etc. The construction works and improvements would continue until 1916.

Stationed Units

During peacetime the Feste formed the garrison of the III. Bataillon des 4. Unter-Elsässischen Infanterie -Regiments Nr. 143 from Mutzig . Every year during four weeks the Badische Fuss- Artillerie Regiment 14 exercised in the Feste .
Early in the war, around 12 August 1914, 3 battalions of the Reserve Infanterie Regiment 60 with components of the Badische Fußartillerie Regiments 14 from Strasbourg, and the 8. Kompanie of the Hohenzollernschen Fußartillerie -Regiment 13 from Breisach am Rhein took over the fortress. Together with artillery teams, maintenance and communication troops, during the war some 6.500 men were stationed in the fortress.

Later during the war several Bavarian “ Landsturm Bataillone ” would alternately be stationed at the Feste above Mutzig . For example; these soldiers of the Bavarian Landsturm Infanterie Bataillon Wasserburg , a component of the Bavarian 36. Reserve Division, were stationed at Mutzig in 1916.

18 August 1914 - 291 Artillery Salvo's

During the Great War the Feste Kaiser Wilhelm II never endured an attack or a siege. The only feat of the Feste happened on 18 August 1914, when the 105 mm. guns fired 291 salvo’s on approaching French troops near Urmatt , some 7,5 km. away to the west, in the Valley of the Bruche .
The Guided Tour
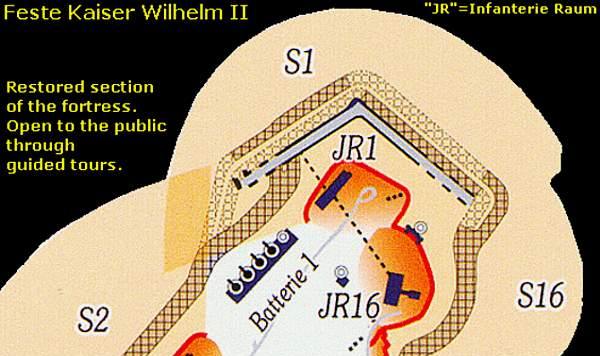
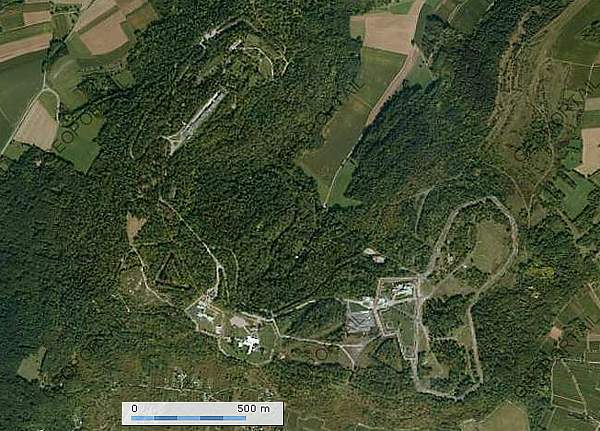
The main part of the height is still French military terrain and not accessible to the public. Only some 10 percent of the fortress complex, the northern site, is open to the public under guidance of well informed, bilingual guides of "Der Förderverein Feste Kaiser Wilhelm II". The visit to the Feste lasts 2,5 hours! We will have to walk at a steady pace for about 3.5 km., much of it underground, and we will have to climb many stairs. We will find original equipment like kitchens, power generator rooms, a bakery, etc. The inner temperature level underground is constant at 12-14° Celsius.
At the entrance of the Feste you have the option for a French spoken tour or a German spoken tour. To get in the right mood for this German fortress we choose of course for the German tour. In a group of about 35 persons we follow this guided tour, which makes it difficult for me to shoot photo’s without other tourists. But anyhow, as you will see later on this page, I know to overcome this problem!
Route
The tour will lead us from the dry moat to the entrance at MG Grabenwehr GrWr1 , to lead us via a tunnel undergound into Infanterieraum JR1 , next underground to Infanterieraum JR 16 , to visit again above ground Schützengraben S16 , a Beobachtungspanzer , Schützengraben S1 , Infanterieraum JR1 outdoors , and Batterie 1 .
( Period photo's of Landsturm Infanterie Bataillon Wasserburg , fieldpostcards send from Mutzig ; courtesy of my Australian friend, Brett Butterworth.)
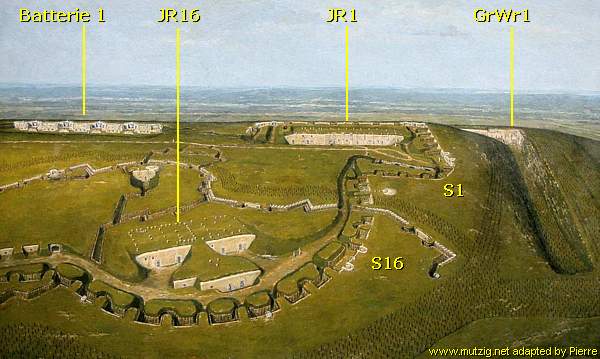
We resume our exploration at Maschinen-Gewehr Kasematte GrWr1 (Construction: 1914). The corner of the moat forms a fortified inner gate, ...

... which the French call a " coffre de contre-escarpe ", or a counterscarp gallery.

The counterscarp gallery controlled with machine guns the dry moat against invaders.

We enter the fortress via this Maschinen-Gewehr Kasematte GrWr1.
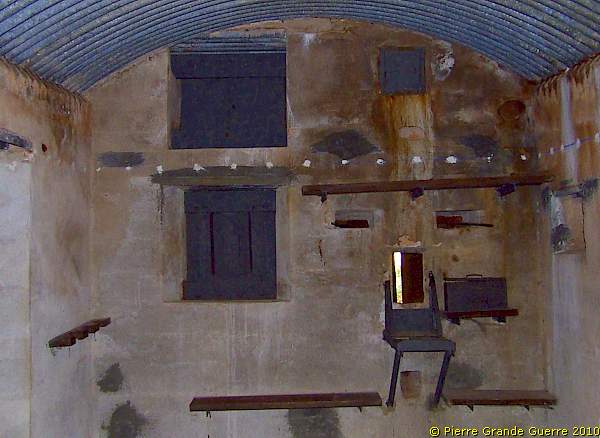

The defenders positioned themselves at the shelves. They mounted their machine-gun at the platform to the right on the photo above.
This counterscarp gallery is connected to the fortress via a tunnel, running beneath the moat.
We descend some 20 m. underground, and we follow a tunnel southward to...

... Infanterieraum JR1 - Infanterie Barracks 1 (1899-1910).

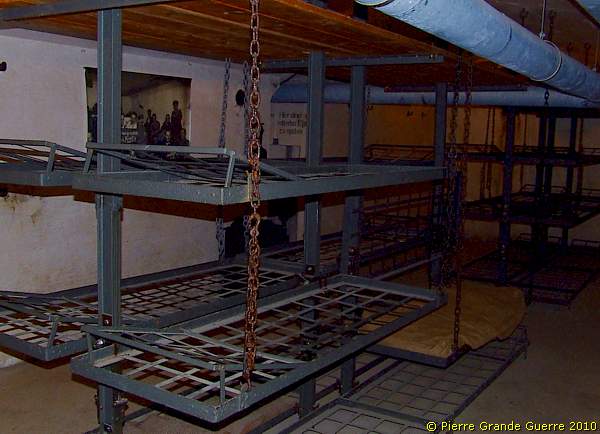
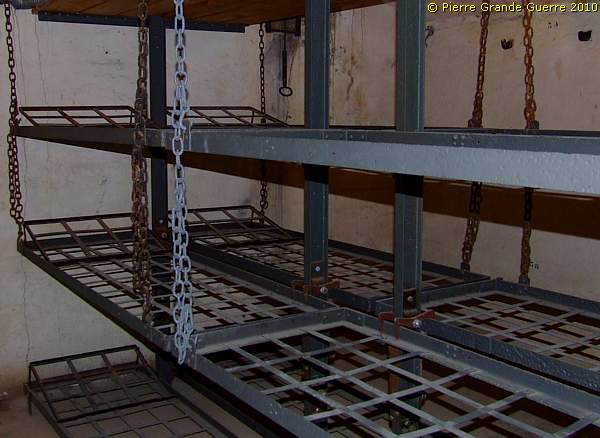
We enter one of the dormitories of JR1 ...
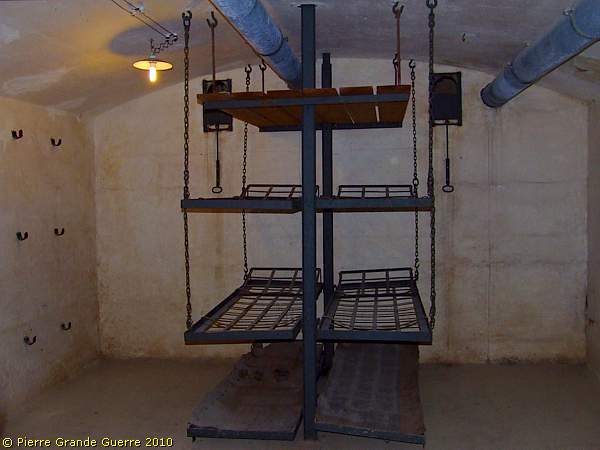

... with bunk beds hanging on chains from the ceiling.


In a corner of the dormitory is a modest exhibition of various types of rifle shields, used on the parapets of the trenches.

Anywhere on the walls you may read (restored) German inscriptions, like this one:

Or:

Two of the underground rooms of JR1 contain a modest exhibition. The second room shows a 3D-model of the Feste and on the walls hang some artist impressions.

The first room shows cross section models of the 150 mm. gun turrets of Fort West and Fort East.
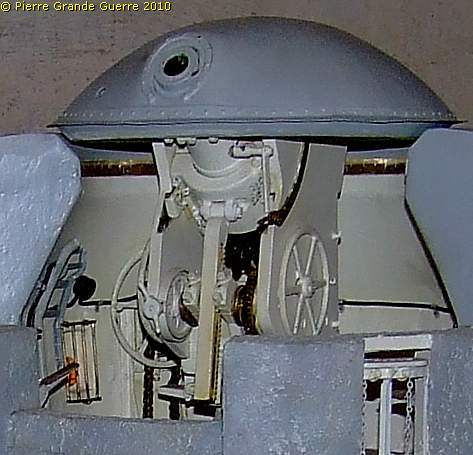


Besides these models the exhibition shows original equipment, ...
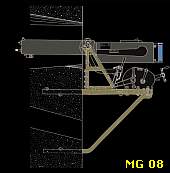
... like this 57 mm. artillery gun, also used on rails in the trenches.

Also: tools and shells in an elevator of the 105 mm. guns.
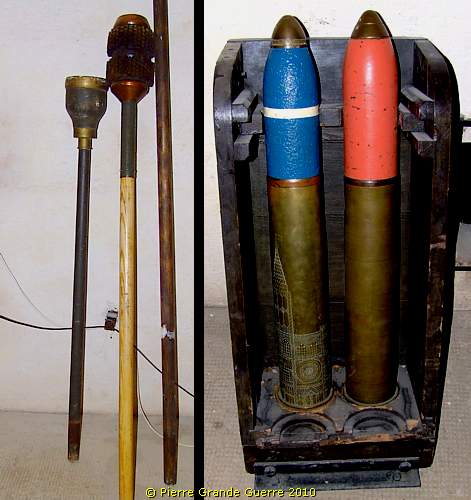

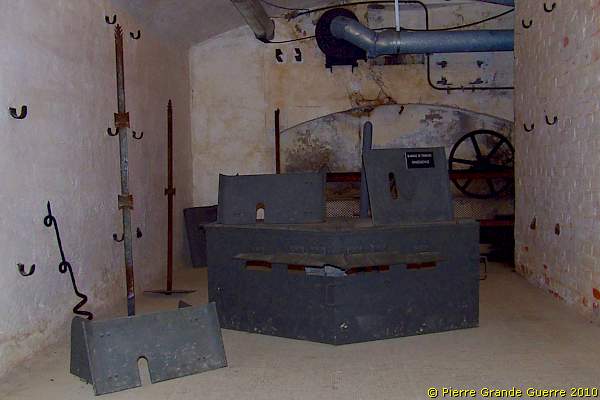
Two light armored observation cupola's, also used on rails, ...

... which could quickly turn around.

We continue underground in JR 1 ...

... to the location of the telephone switch board.


Next we enter a storage room.



There is shaft to a lifting device downstairs.
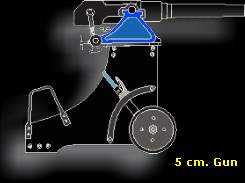
We descend to a lower floor and follow a narrow corridor to...

... a generated lifting device.

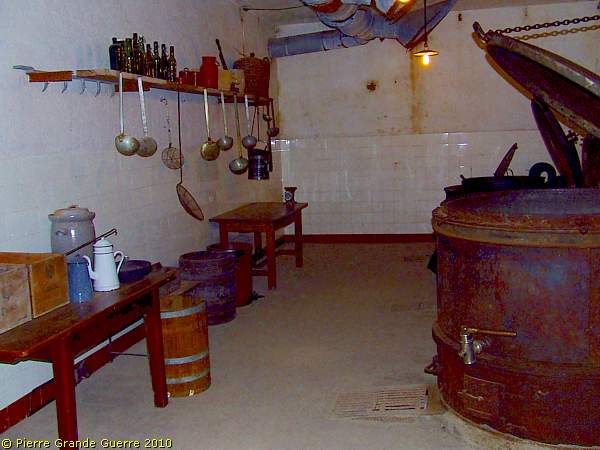
In a next room we find the kitchen of JR1, ...
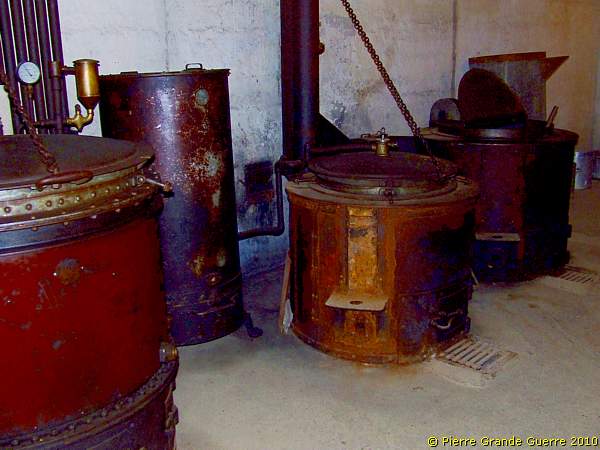

... with exception of the rust, the kettles look like these have been left only yesterday.
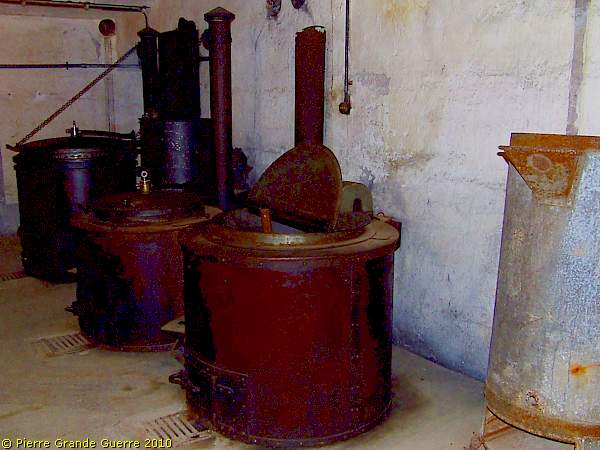

We leave JR1 and follow a long, connecting tunnel to JR16.

Infanterieraum JR16 - Infantry Barracks 16 (1913)
In JR16 we arrive at the bakery.
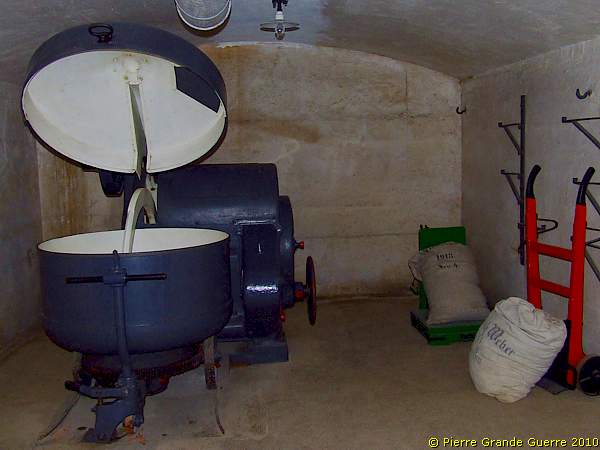

Being a grandson of a baker I was particularly interested in this 100-years old, German dough mixer, ...

... and the oven, originally designed for use in ships.
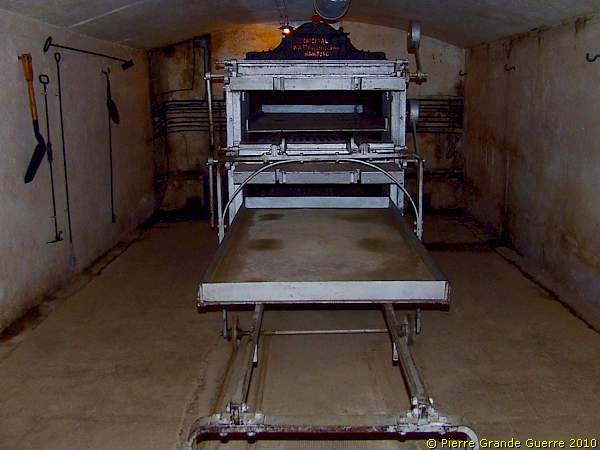

We continue and approach the heart of JR16.

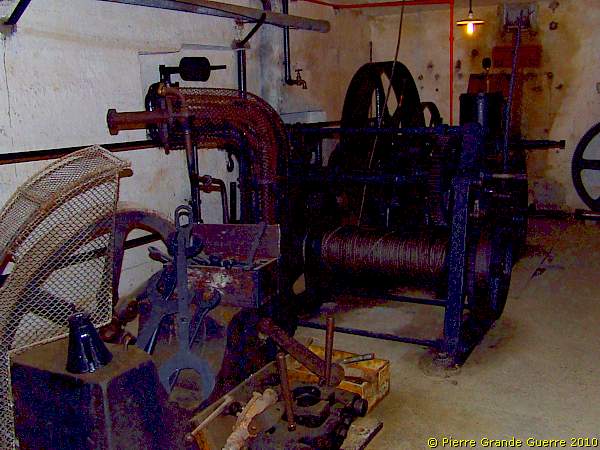
We enter the maintenance workshop of the electricity power station.

A turning lathe.
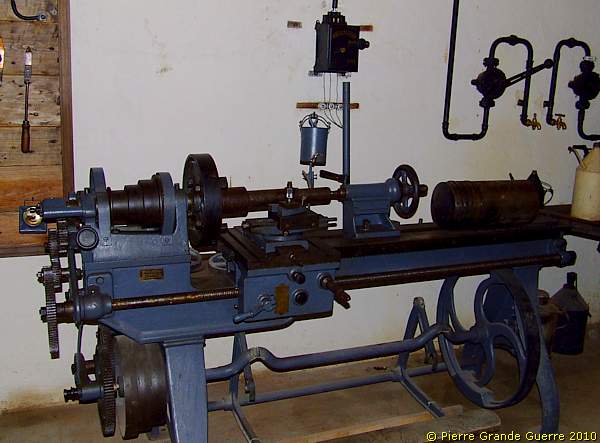

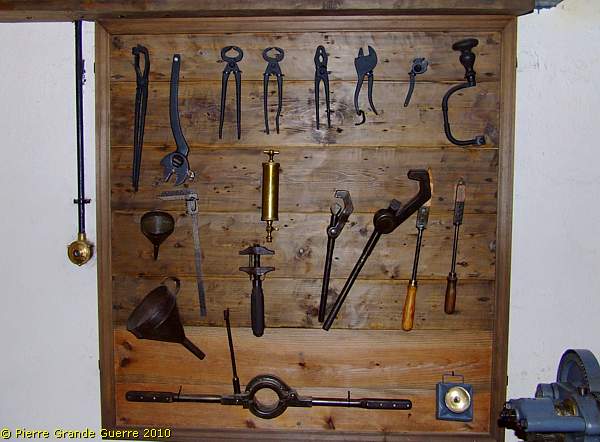
1918-Style tools-board.




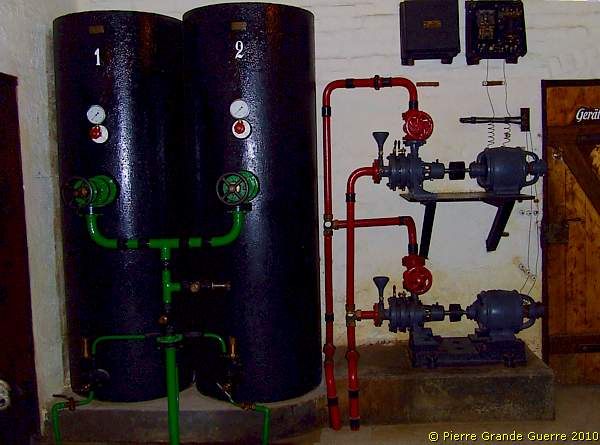
Diesel oil containers 1 and 2 are connected to generators 1 and 2 in the next generator room. The colour code of the pipelines seems rather important.

These 100-years old installations are extraordinarily and beautifully restored.
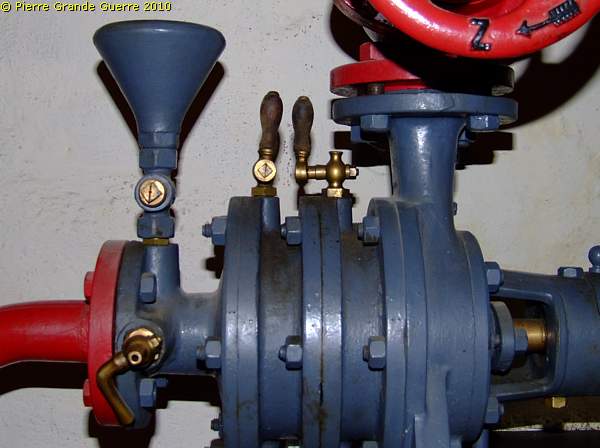

This manometer looks like it has been manufactured yesterday.

In the next room we enter the real heart of the fort; ...
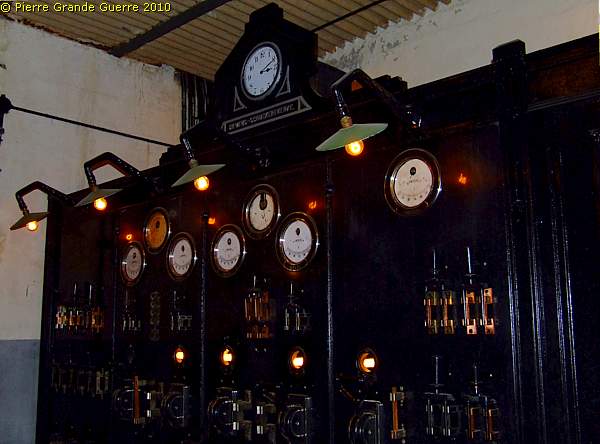

... the power station with it's splendid control panel.
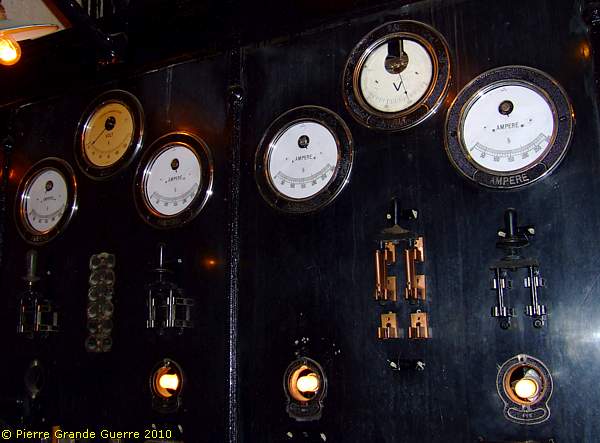

Of course next to the water supply electricity power was vital.


Next to the control panel stand 4 identical generator engines.

Due to the steady pass of our guide, ...
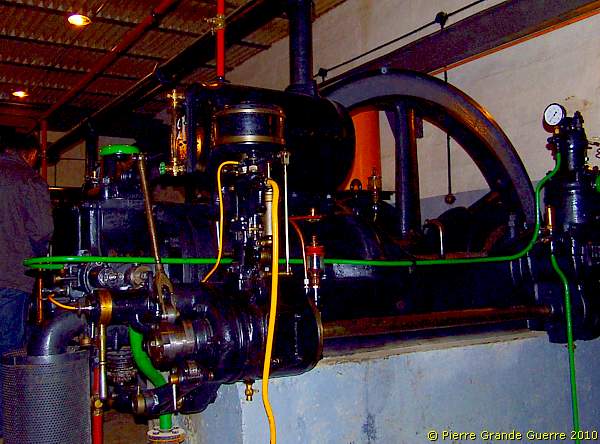

... I can only show you number 1 and number 2.

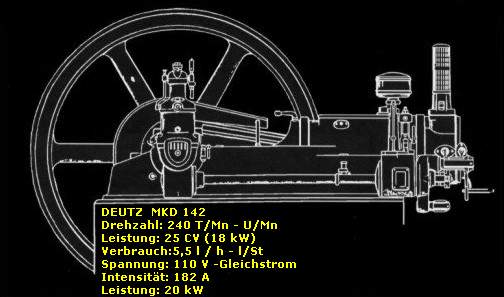
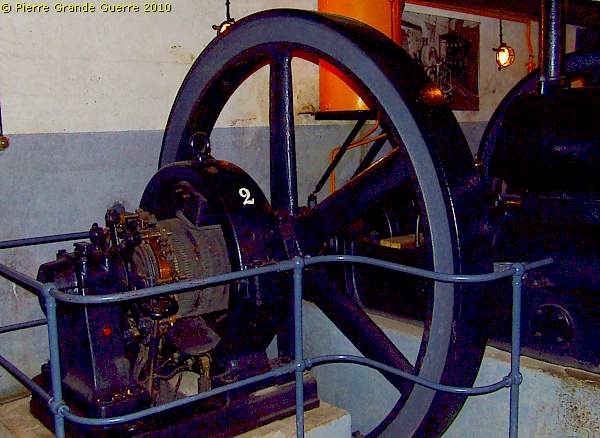
We are still in the "Keller Geschoss ", the cellar.

The next rooms, we will visit, come together in this corridor.
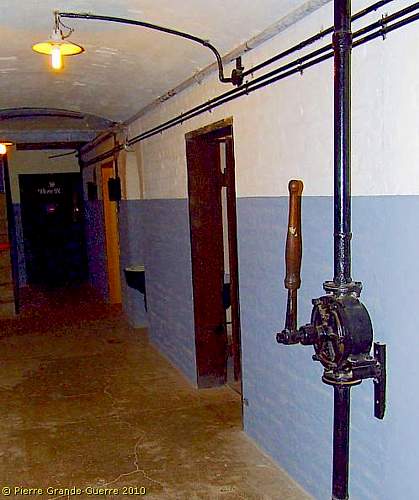

The door of the First Aid Post or Lazarett.

The surgery room.
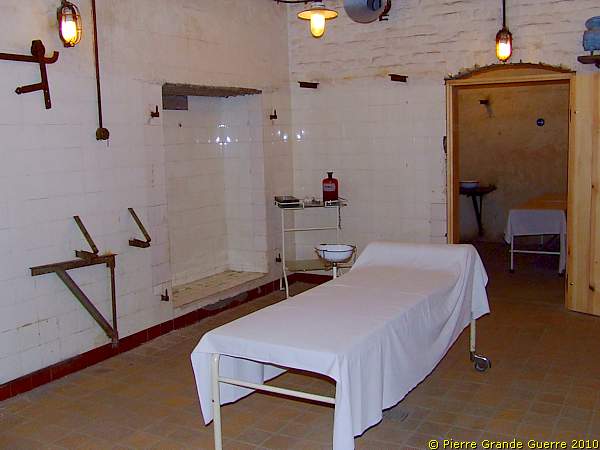



In the next room German, 1918-style "intensive care".
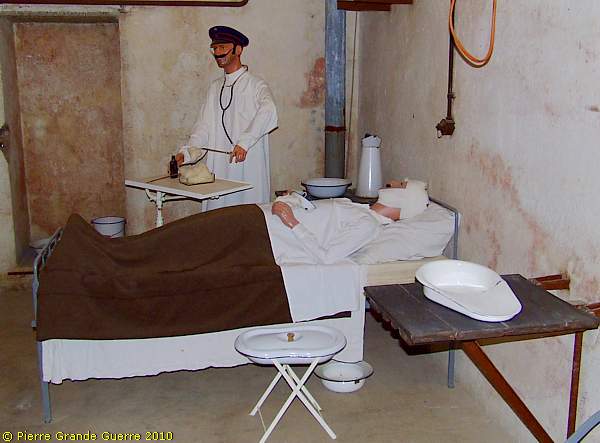
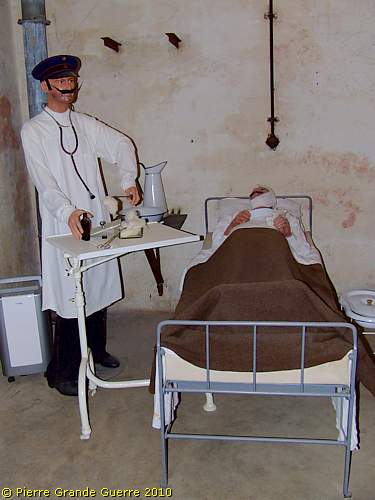
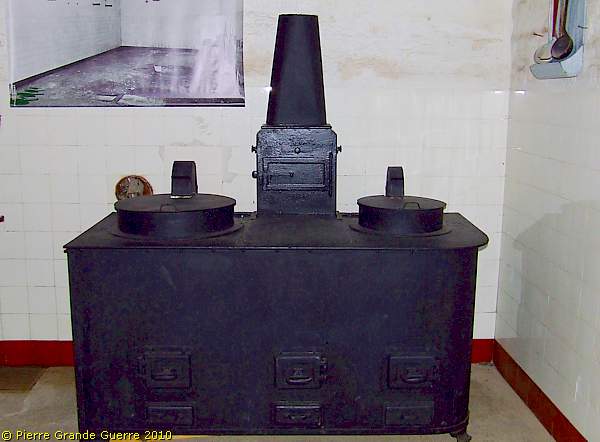
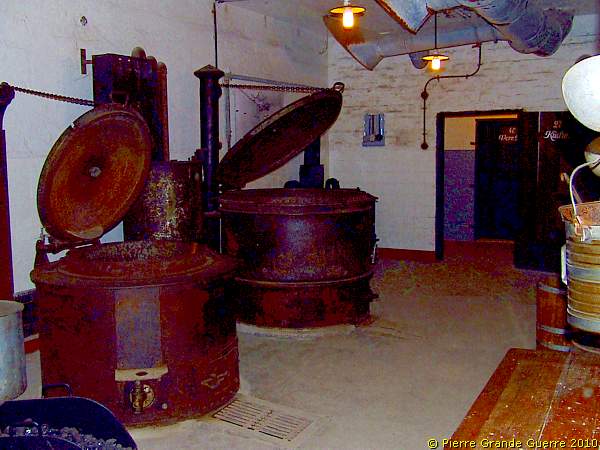
Through this door we enter the kitchen of JR16.
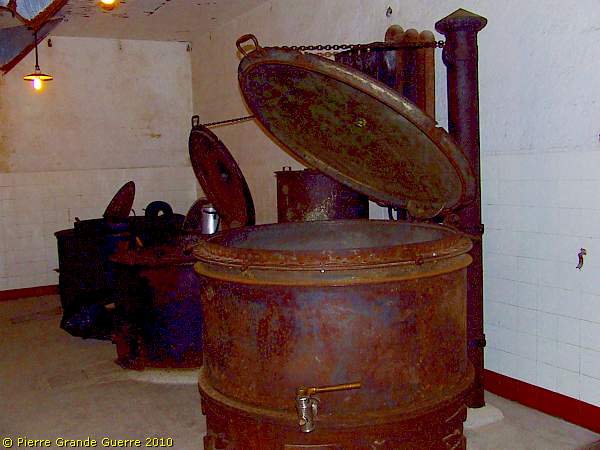



The stove.


Leftovers bin.


Back in the corridor we find some interesting electricity relay stations, ...

... and fuse boxes.

Room 44 is an officers bedroom.
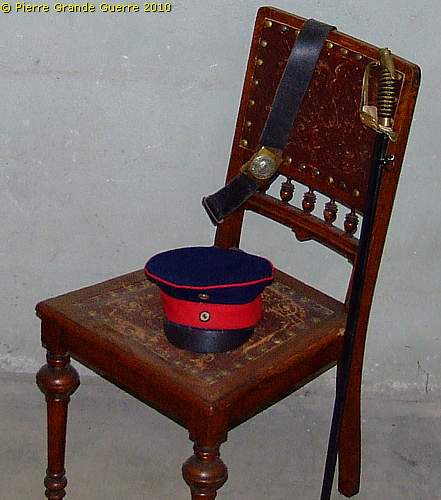





Routing direction:

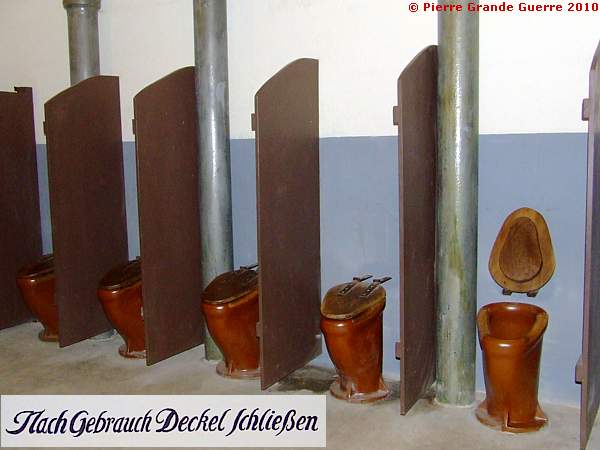
Another bare necessity of life: Latrines.
Notice: In contrary to their French opponents, who traditionally had to squat above a hole in the ground, the German soldiers enjoyed the luxury of hygienic chamber pots with a lid.

We climb many stairs, ...

... and we walk through long corridors to an above ground exit.

From now on we continue our visit outdoors.
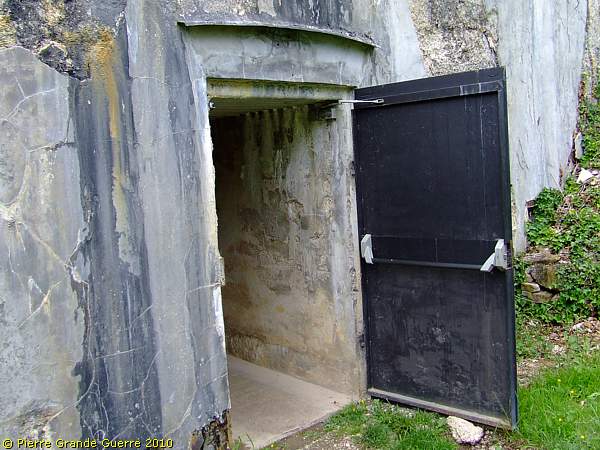


The north exit of JR16.


From JR16 we enter Schützengraben 16 (1900-1915), Trench 16.



A snail house-shaped observation post.
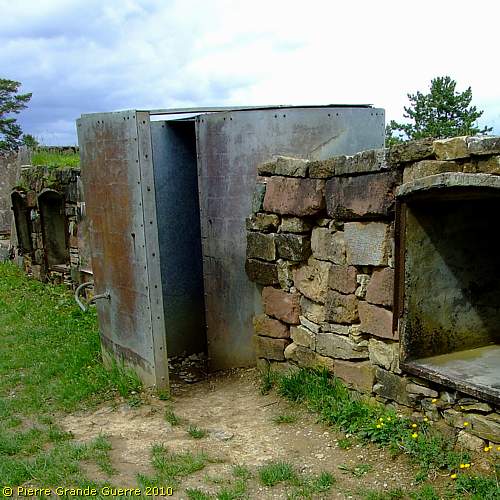

Rails to mount an artillery gun like the 57 mm. guns.


An exit of the tunnel system.
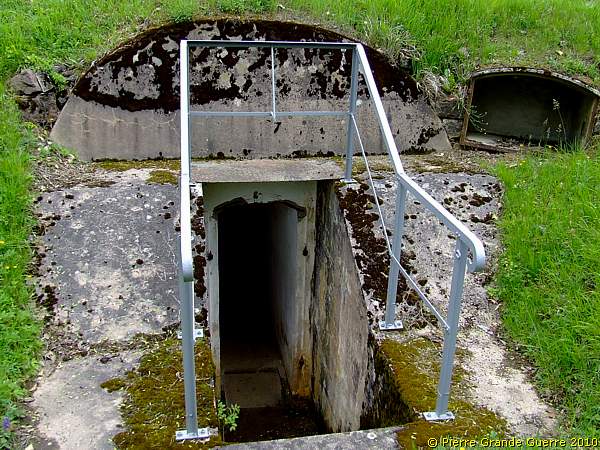

We pass this interesting Panzerbeobachtungsstand (1898), ...

... an armored observation post.
The panorama view westward from the observation post.

From the observation post we enter Schützengraben 1 (1900-1915), Trench 1, passing one of the many tunnel exits.
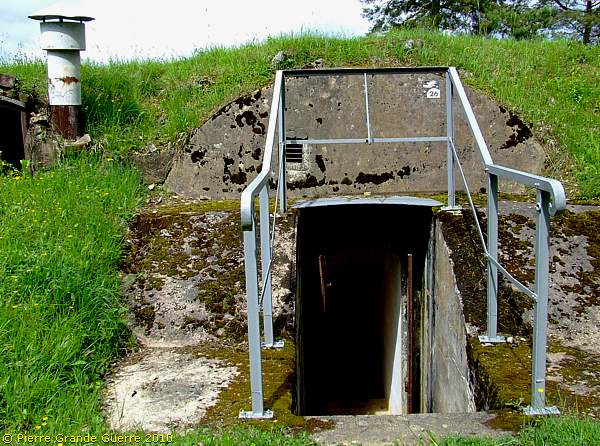

A view north-westward over Schützengraben 1.



We go westward and we see the shellproof top construction of ...

... Infanterieraum JR1 .

From JR1 we approach our last site of our visit to the complex of the Feste Kaiser Wilhelm II: Batterie 1 - Battery 1 (1899).



Batterie 1 possesses four 105 mm. guns.
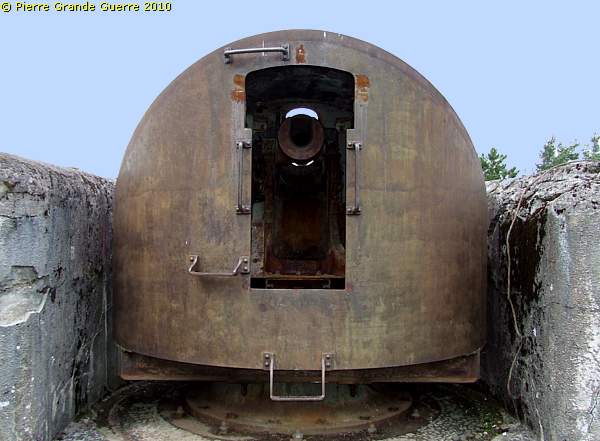


View westward.

At the right side of the guns: an observation cupola.

These guns were only one time engaged in a battle: on 18 August 1914, firing 291 salvo's at the Bruche Valley.

While our tour ends here, the weather changes dramatically.

Just before the rain arrives, a last view westward from the Feste Kaiser Wilhelm II.

Continue to the next Special Photo Impression: "ALSACE - General Gaede's Tactical Significance - WFA-NL Lecture"










